Cervical Dysplasia
‘Cervical’ refers to the cervix, which is the neck of the uterus that juts into the top of the vagina. ‘Dysplasia’ means that cells are growing in a disorganised unhealthy way. Cervical dysplasia is thus a term which describes pre-cancerous or potentially cancerous cell abnormalities of the cervix, usually picked up on a pap smear. Patients with cervical dysplasia will often say that they have an abnormal PAP smear.
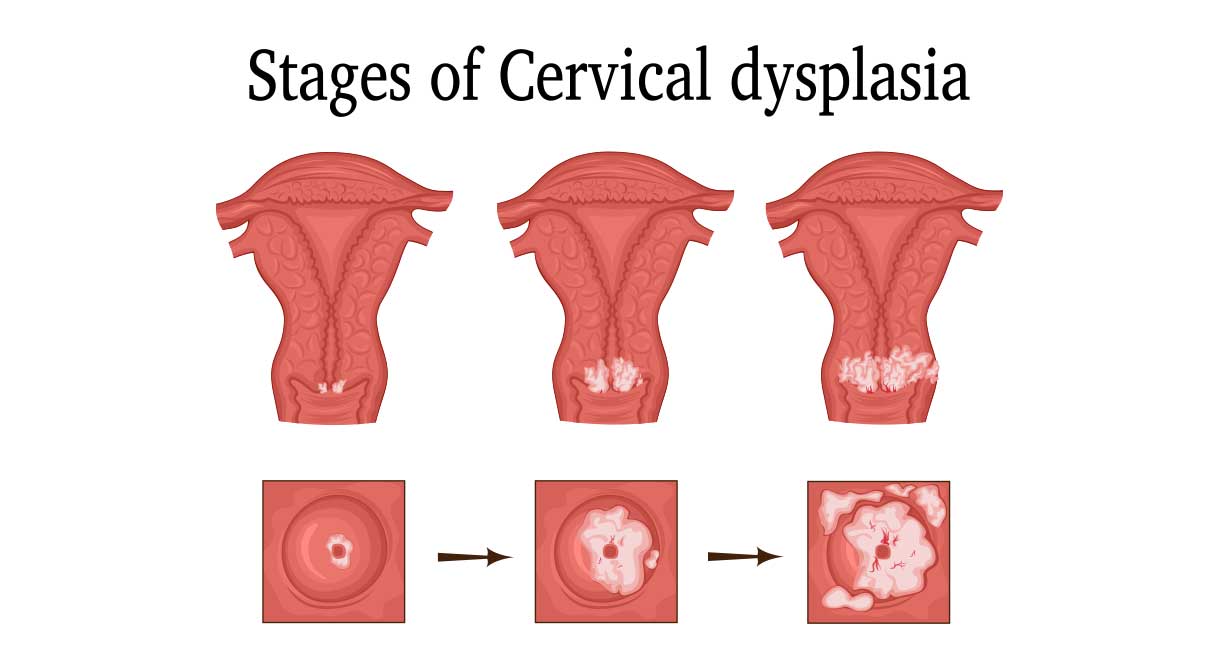
The term ‘Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia’ (CIN) is also used to describe these pre-cancerous changes, and is graded from 1 to 3 to depict the degree of abnormality. CIN 1 = mild dysplasia, CIN 2 = moderate dysplasia and CIN 3 = severe dysplasia.
To confirm the diagnosis made via the pap smear, a more definitive test called a colposcopy is usually performed. This is where the cervix is examined using a special microscope (colposcope). The doctor paints the cervix with acetic acid (a vinegar-type solution) and then a dye, which will show up any abnormal lesions. From the patient’s point of view this procedure is just like having a PAP smear, in that a speculum is inserted into the vagina. The colposcopy itself is painless and takes about fifteen minutes. If necessary, a small biopsy (tissue sample) may be taken from a suspicious area and examined by a pathologist to give an accurate diagnosis.
What causes it?
Cervical dysplasia is usually caused by infection with the wart virus known as the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). Around 80% of people will be infected with at least one type of genital HPV during their life. There are more than 100 types (strains) of HPV with over 14 strains being able to cause cancer. The type of HPV you carry can be tested from a swab taken from the cervix when you have your PAP smear.
The HPV virus can cause cancer of the throat, mouth and tongue.
Treatment
It is not a certainty that all cases of cervical dysplasia will develop into a cancer; indeed most do not. In many instances our immune system deals with the abnormality and the cervix returns to normal. For this reason, mild dysplasia (CIN 1) may be treated conservatively and just observed via repeated PAP smears or a follow-up colposcopy. Whether this approach is taken is usually a matter for discussion between you and your doctor. For moderate to severe dysplasia (CIN 2 and 3), treatment aimed at removing or destroying the abnormal cells will usually be recommended. These treatments include laser vaporisation, electrocoagulation diathermy or cryotherapy (freezing). To help eradicate mild dysplasia, or prevent a recurrence after treatment, the following nutritional and lifestyle changes are highly recommended. They must, of course, be accompanied by regular follow-up PAP smears to check your progress.
General recommendations
Avoid smoking as it increases risk of cervical cancer.
Try to relax and get plenty of regular sleep. Yoga, Pilates and meditation are beneficial, possibly using visualization techniques where you see the abnormal cells being replaced by new healthy cells. This may sound fanciful but the power of the mind is often underestimated!
Do some outdoor exercise as you need vitamin D for a healthy immune system to prevent cancer.
Diet
Include often – fresh fruits and vegetables, preferably organically and/or locally grown; if not organic, then wash them well to remove pesticides. Raw nuts and seeds are a good source of minerals. Avoid – refined sugars; white flour products, fried foods and margarine.
Raw juicing
Raw juices based on carrot are beneficial as carrots are rich in beta-carotene (a precursor of vitamin A) – diets deficient in Vitamin A have been associated with an increased risk of cervical dysplasia. Beta carotene is vital for the health of the mucous membranes.
The following juice recipes from the book Raw Juices Can Save Your Life are recommended:
Juice for Cancer Patients
Ingredients
- 2 spinach or 2 dandelion or 2 kale leaves
- 1 orange
- 1/2 papaya
- 1 carrot
- 1 clove garlic or 1 spring onion – optional
- 1/4 beetroot
- 2 shiitake mushrooms (remove stems and wipe caps clean)
Method
- Wash, chop and pass through juicer.
Immune Booster Juice
Ingredients
- 1 stick celery
- 1 ripe tomato
- 1 pear
- 1/4 beetroot
- 1 lemon or 1 lime
- 1 grapefruit
- 1 carrot
- 2 dandelion leaves or 2 cabbage leaves
- 1/2 inch (1.5 cm) slice fresh ginger
- 1 clove garlic or 1/4 red onion (optional)
Method
- Wash, trim and chop and process through juicer.
Orthodox medical treatment
For mild dysplasia a more conservative approach is adopted via repeat PAP smears and colposcopy. Moderate to severe dysplasia is more serious, and definitive treatment is usually undertaken to avoid the risk of progression to cervical cancer. The abnormal cells are removed via laser, diathermy or freezing. This can often be performed in the gynaecologist’s consulting room, or may require a day stay in hospital. If the abnormal cells appear to extend up the endocervical canal a ‘cone biopsy’ may be required. This involves the surgical removal of a cone-shaped section of the cervix. Prognosis is excellent following these treatments. However, repeat PAP smears at three to six monthly intervals will be required for one to two years.
Recommended supplements for cervical dysplasia
Antioxidant nutrients form the basis of a supplement program for the prevention of cancers. Research has suggested that antioxidants may help to protect against cervical cancer. Selenium is a mineral with unique and powerful anti-viral properties and viral infections are much more virulent in a selenium deficient host. Indeed many viruses can be stopped from causing different types of cancer simply by giving a daily protective dose of selenium
- Selenomune
Take 1 capsule daily. Selenomune is the leading selenium supplement for the immune system and has powerful anti-viral and cancer-protective effects. - MSM Plus Vitamin C Powder
Take 1 teaspoon daily to strengthen the immune system. - Vitamin D
Take 2,000 to 5,000 I.U. daily with food. Make sure you are not low in vitamin D. Vitamin D helps to encourage healthy cell replication. - N Acetyl L Cysteine (NAC)
Take 1 capsule twice daily. N-acetyl cysteine helps to increase production of the body’s own powerful antioxidant called glutathione, which repairs cell damage.
The above statements have not been evaluated by the FDA and are not intended to diagnose, treat or prevent any disease.

Leave A Comment